PNG’S SECOND PHASE LNG DEVELOPMENT AND GAS-FIRED ELECTRIFICATION ARE POISED TO EMPOWER THE PNG ECONOMY
This economic impetus in 2014 enabled the extractive sector, including petroleum and minerals, to overtake agriculture in terms of their dominating role in the nation’s Gross Domestic Product.
According to the International Monetary Fund, in 2014 PNG’s oil and gas sector constituted 11.3% of GDP while mining contributed an additional 9.1%. The combined resource sector 20.4% share of GDP contrasted with 17.8% for agriculture, forestry, and fishing.
The oil and gas share of GDP has grown to 15.4% in 2017 while mining and quarrying shrank slightly to 8.4% for a combined extractives sector share of 23.8% as against 18.2% for agriculture. LNG exports began to kick in at a time when the hydrocarbons sector was losing steam. Output from the country’s mature oil-producing fields at Kutubu, Moran, and Gobe, had been in decline, having fallen from a peak of 150,000 barrels a day when Kutubu came onstream in 1992 to the current oil production averaging around 30,000 b/d.
The country’s LNG production and exports has risen from approximately 7 million tonnes annually in 2015 to just over 9 million tonnes annually in 2018.
In breaking down the overall oil and gas contribution to the PNG economy, the 2019 National Budget prepared by the Department of Treasury estimated that:
- LNG export revenues have risen to an estimated K14.8 billion in 2019 from K9.8 billion in value in 2015;
- Oil production in 2019 in PNG was estimated at 7 million barrels worth K1.68 billion in 2019, compared with 9.5 million barrels in 2016 worth K1.25 billion;
- Condensate exports, which are associated with LNG production, has seen export values drop from K1.5 billion in 2015 to K745 million in 2019 even though production rose slightly from 10.4 million barrels to an estimated 11 million barrels.
Gas development agreements for the Papua LNG Project, which will involve development of the Elk-Antelope gas fields in Gulf Province; and for the P’nyang gas field, 130km northwest of Hides, the key gas resource for the PNG LNG Project by mid-2019.
The Papua LNG project, led by Total Oil (40.1%) and including ExxonMobil (37.1%) and Oil Search (22.8%), will involve construction of two LNG trains, while P’nyang will support an additional train that will represent an expansion of the existing PNG LNG Project. Each of the three trains will have a capacity to produce 2.7 million tonnes of LNG annually, effectively doubling PNG’s current level of LNG exports.
The additional 8.1 million tonnes a year LNG capacity, along with associated production of condensate, will fuel a substantial boost to the PNG economy in the coming decade. The three new LNG trains are expected to be completed in 2024.
The PNG Government plans to set aside some 5-15% of available gas under a Domestic Market Obligation will provide a further major boost to the nation’s economic fortunes through a substantial electrification program and the prospect of attracting investors for petrochemical production.
At the APEC Summit in Port Moresby in November 2018, PNG joined hands with four countries – the United States, Japan, Australia and New Zealand –to form an Electricity Partnership with the aim of greatly increasing the country’s power generating capacity and making electricity accessible to the wider population.
Although significant gas-fired power generation has commenced in Port Moresby, it is estimated that only 13% of the 8 million plus population currently have access to electricity. The Electricity Partnership has set an ambitious target of making power available to 70% of the population by 2030.
The resilience of PNG’s oil and gas sector was clearly on display in the wake of a devastating 7.5 magnitude earthquake that struck the Highlands region on 26 February 2018. The epicentre in the key oil and gas producing areas in PNG’s Highlands. Despite an eight-week shutdown of gas production, LNG output bounced back to levels beyond those prior to the earthquake by the final quarter of 2018.

Key players in PNG’s Oil and Gas sector

Operator of the PNG LNG Project with an equity stake of 33.2%; ExxonMobil also has a 37.1% stake in the proposed Papua LNG Venture and a 49% stake in P’nyang.
Equity holdings in Papua LNG and P’nyang will be reduced on a pro rata basis when the PNG Government, as expected, opts to take up a 22.5% stake in these ventures.
Additionally, ExxonMobil has significant stakes in newly discovered gas resources at the Muruk field, not far from Hides, and significant onshore and offshore exploration permits, including deep water prospects where no drilling has been undertaken to date.
http://www.pnglng.com

Operator of PNG’s oilfields, which are located mainly in Southern Highlands, is PNG’s oldest operating company with a petroleum exploration history that dates back to 1929. It is the second largest equity owner in the PNG LNG Project with a 29% stake, along with 28.2% in Papua LNG and 38.5% in P’nyang.
Oil Search is also a major partner with ExxonMobil in the highly attractive Muruk gas field and in 2018 undertook the largest onshore seismic program in its history. It also holds significant onshore and offshore exploration permits.
With all its oil and gas production based in PNG, Oil Search took a big step in November 2017 to invest US$400 million in the Alaska North Slope, where it has assumed operatorship of undeveloped oil discoveries that have been described as the largest conventional oil discoveries in the United States in the last 30 years.
Appraisal and exploration programs are underway and front-end engineering and design work is anticipated to commence in 2019 for its Pikka development unit.
http://www.oilsearch.com

The French multinational, Total Oil, a relative newcomer to PNG exploration and production, will be the operator of the Papua LNG Project, where it currently holds a 40.1% equity stake. Total has also extensive exploration acreage and has committed itself to drilling PNG’s first ultra-deep offshore exploration well in the Gulf of Papua.
http://www.total.com

The PNG Government’s national oil company, Kumul Petroleum, is the third largest partner in the PNG LNG Project, with a 16.8% stake.
It has an option to take up a 22.5% equity on behalf of the PNG Government in the Papua LNG Project and in P’nyang.
The company is in a 50:50 joint venture with Oil Search, NiuPower, which has completed construction of a 58-megawatt gas fired power station in Port Moresby. Gas is supplied by the PNG LNG Project.
http://www.kumulpetroleum.com

Australia’s Santos Ltd has a 13.5% stake in the PNG LNG Project. It has 9.4% equity in the Southeast Gobe oil field with expectation that it will farm into the P’nyang gas discovery.
http://www.santos.com
The company has conducted appraisal drilling of the Pasca gas-condensate field in the offshore Gulf of Papua, where it expects to host PNG’s first offshore field development. The Pasca discovery was made in 1968. Twinza took up the exploration permit covering the area in 2011.
An updated field development plan has placed certified proven and probable reserves at 69.1 million barrels of condensate and liquefied petroleum gas along with 2-C resources of 326.7 billion cubic feet of natural gas. The project is awaiting the green light from the Department of Petroleum.
http://www.twinzaoil.com
Petroleum Projects Map
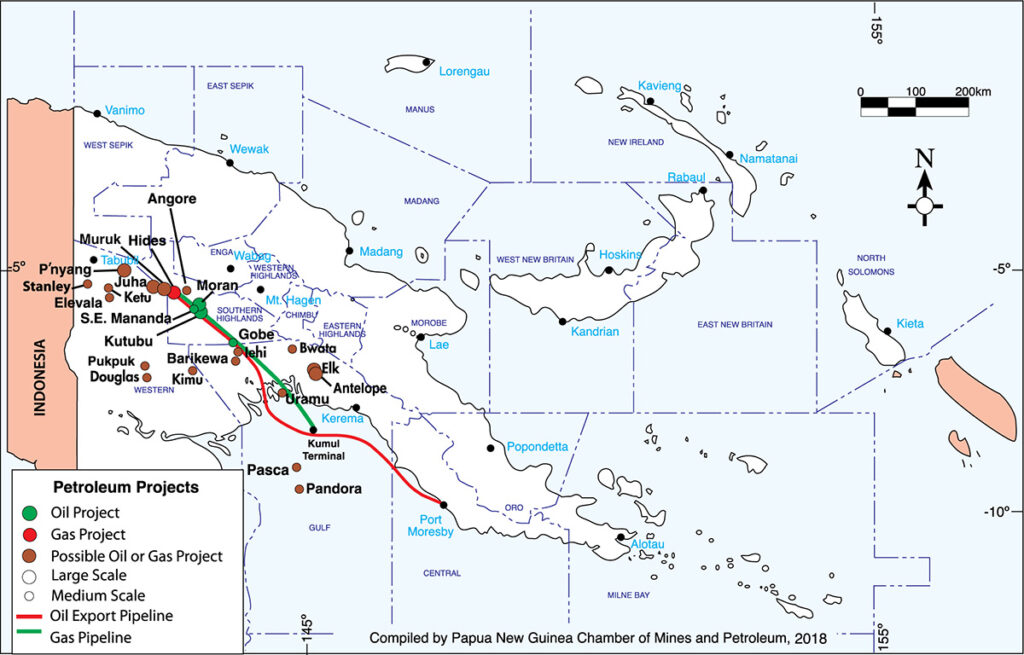
Other companies involved with exploration and with equity stakes in a number of stranded gas-condensate fields such as Elevala, Ketu and Stanley in PNG’s Forelands Region include Horizon Oil and Kina Petroleum, which are listed on the Australian Stock Exchange.
Fact Sheet
20000
+No. of Papua New Guineans employed directly through mining & petroleum industry
84
%Industry Contribution to PNG’s Export Revenue valued at PGK 23 Billion
30000
+No. of Jobs the Industry Supports in Landowner and Local Businesses
26
+Industry Contribution to Papua New Guineas's Gross Domestic Product
How much is the industry contributing to
Papua New Guinea?
The mining and petroleum industry is an important contributor to Papua New Guinea’s development. The industry has underpinned the PNG economy for decades, providing considerable social and economic benefits that have flowed to the government and the people of PNG.

Mining
Papua New Guinea has a well-established mining industry, attracting investment from many of the world’s leading mining companies.

Petroleum
The country’s LNG production and exports has risen from approximately 7 million tonnes annually in 2015 to just over 9 million tonnes annually in 2018.

Social Contributions
Mining and petroleum companies invest millions of Kina in community development programmes in their host communities and provinces.

Economic Contributions
The mining and petroleum industry have long played a vital role in Papua New Guinea’s economic development.


